|
|
Cross+A  Variații de puzzle Variații de puzzle
Slitherlink In Sheep and Wolves the diagram contains the black circles ("sheep") and the black crosses ("wolves"). All sheep are supposed to be contained within the loop, while all the wolves should be kept outside.
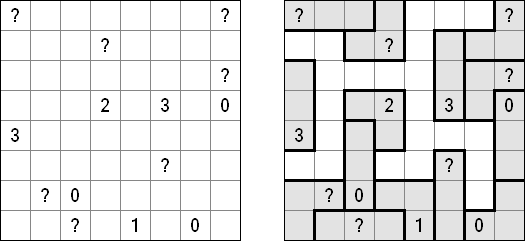
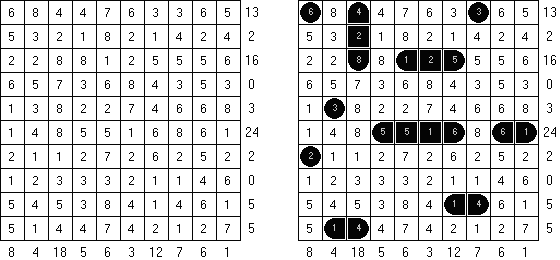
Battleships In Digital Battleships all cells of the grid contain numbers. The values on the right and bottom edges of the grid reveal the sum of the numbers in each of the ship pieces that appear in each respective row or column.
Retrograde Battleships ("Reverse Battleships") contains all segments of the ships in the grid. The aim is to find the correct locations of the ships. No ship may touch another, even diagonally.
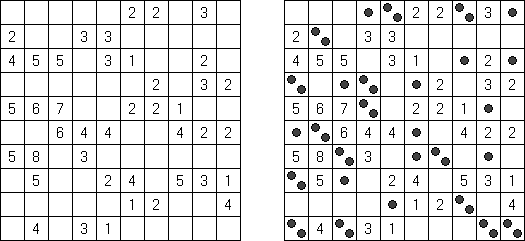
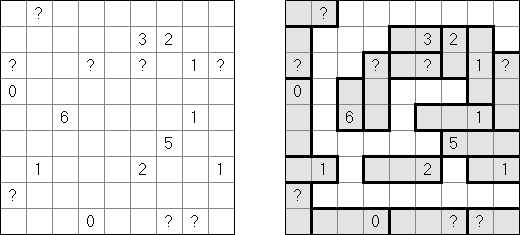
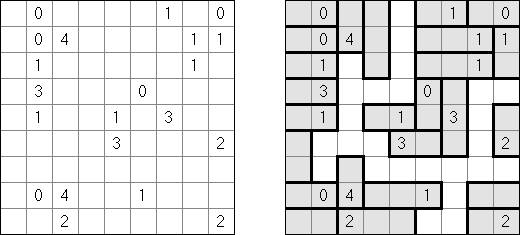
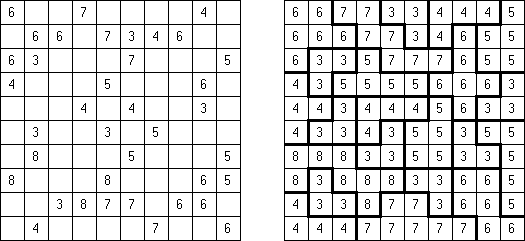
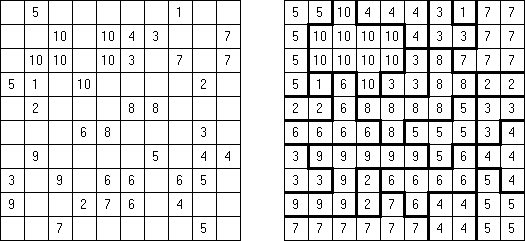
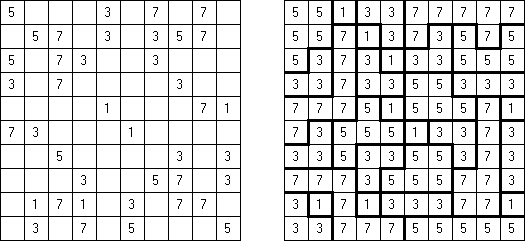
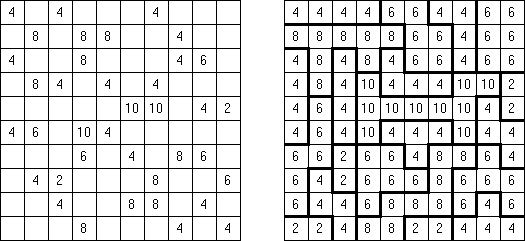
Fillomino No Rectangles Fillomino: rectangular regions are not allowed.
Only Rectangles Fillomino: all regions must be rectangular.
No 2 x 2 Squares Fillomino: no 2 x 2 cell area within the grid can contain the same numbers.
Non-Consecutive Fillomino: any two adjacent regions must differ in size by at least two.
Consecutive Fillomino: any region of size N must be orthogonally adjacent to at least one other region of size N-1 or N+1.
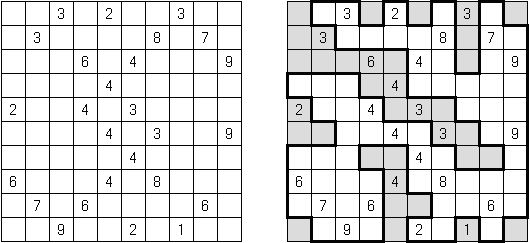
No Row/Column Repeats Fillomino (also known as "Deadomino"): in each row and each column all cells with the same number must belong to the same region.
All Odds Fillomino: the size of each region must be an odd number.
All Evens Fillomino: the size of each region must be an even number.
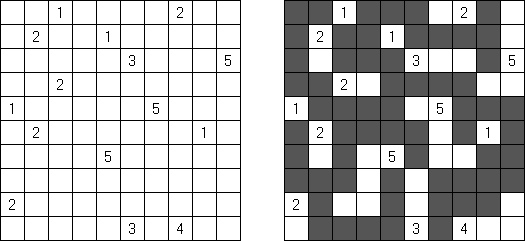
Nurikabe Line Nurikabe: a grid cannot contain five consecutive black cells in a row or column (2 x 2 cell area can be all black).
Pairs Nurikabe: each island must contain exactly two numbers (instead of one) and have total size equal to the sum of these numbers.
Skyscrapers In Sum Skyscrapers the number outside the grid indicates the sum of heights of visible buildings.
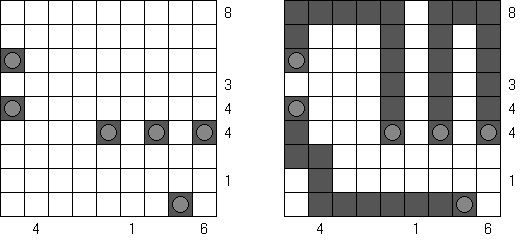
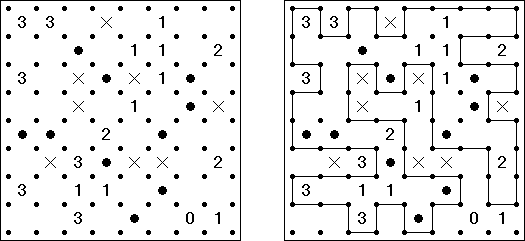
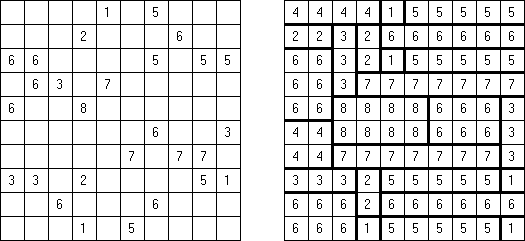
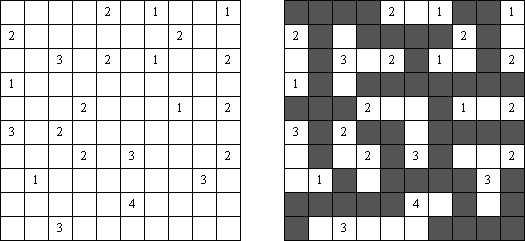
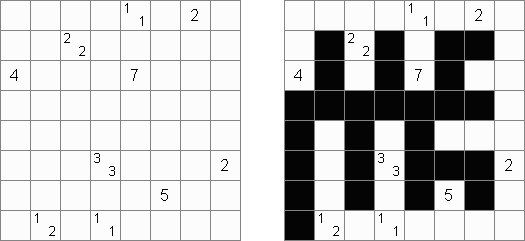
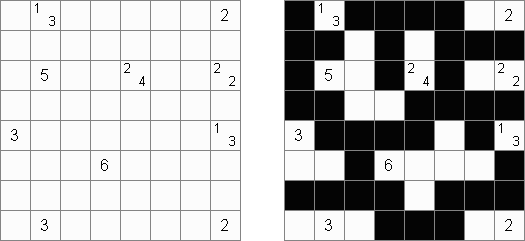
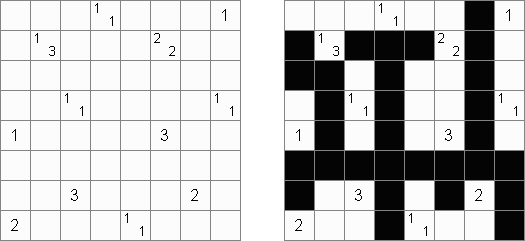
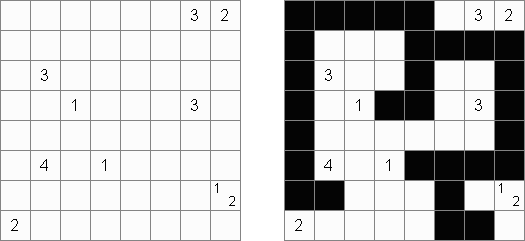
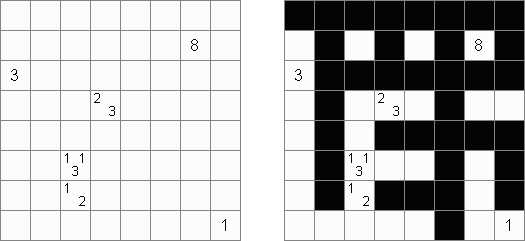
Tapa There are many variations of Tapa puzzle. Some of them can be solved by Cross+A. Tapa [Line]: there may not be four consecutive black cells in any row or column.
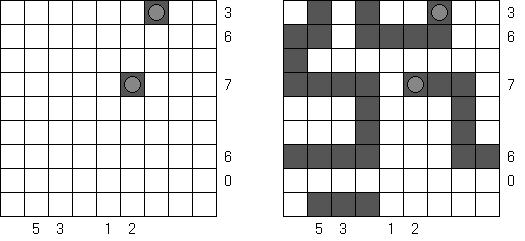
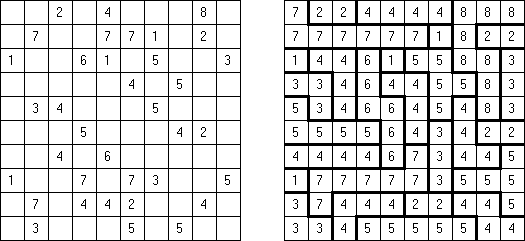
No Squares Tapa: no 2 x 2 cell area within the grid can contain all white cells.
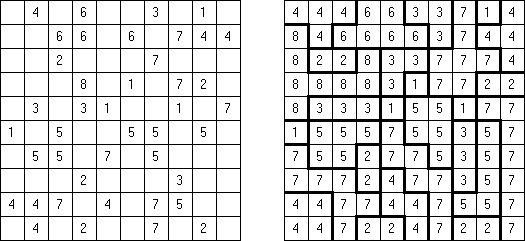
Equal Tapa: the amount of white cells (except clue cells) must be equal to the amount of black cells.
B&W Tapa:
Tapa Islands:
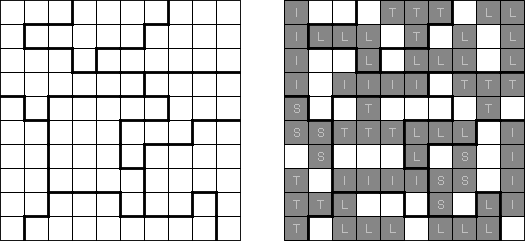
Pata: the clues indicate the groups of connected white cells that are around the square; different groups of white cells are seperated by at least one black cell.
In Tapa Balance the amount of black cells in the left part of the grid is equal to the amount of black cells in the right part. Clues and white cells are considered weightless.
Tapa Row: the sum of all clue digits in the row is equal to the amount of black cells in this row.
Tapa 1-n: all rows and columns should contain different amounts of black cells.
In Dissected Tapa black cells and white cells form two congruent figures. Two figures are congruent if they have the same shape and size.
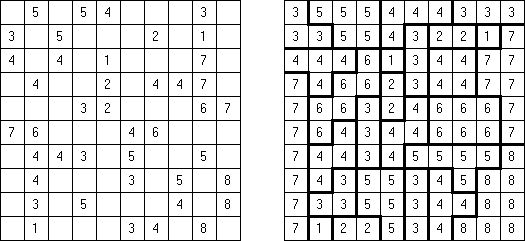
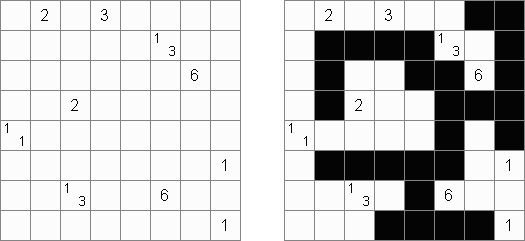
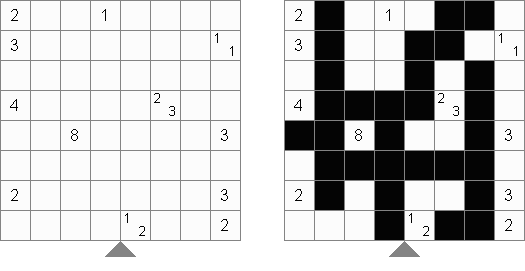
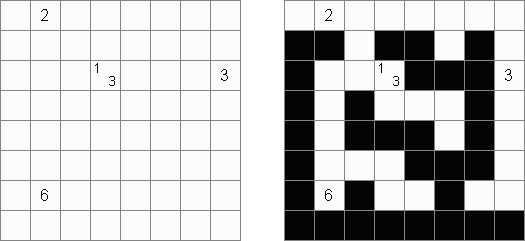
Tapa [Diagonal Neighbors]: every black cell must have at least one diagonally adjacent black cell.
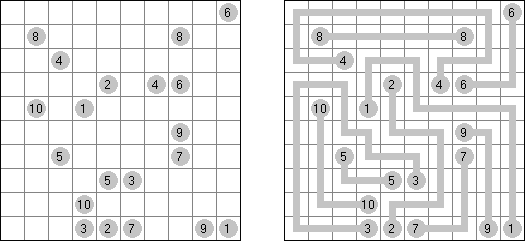
Corral Inside/Outside Corral is a variation of Corral puzzle. The numbers can be inside the loop and outside the loop. In both cases the number indicates how many cells can be seen horizontally and vertically from that cell, including the cell itself.
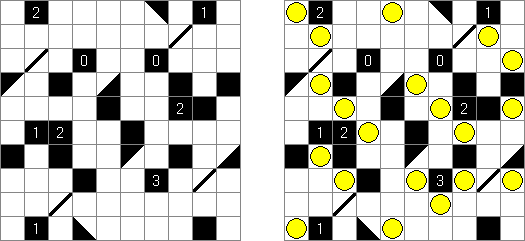
Arukone Arukone3:
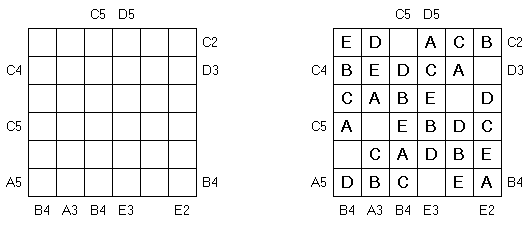
Easy as ABC Not as Easy as ABC is a variation of Easy as ABC puzzle. The goal is to fill in the first letters of the alphabet on every row and every column exactly once. One cell in every row and every column remains empty. Letters and numbers on the outside indicate at what position you come across this letter when looking from that side (e.g. C2 means the C is the second letter encountered when looking from that side).
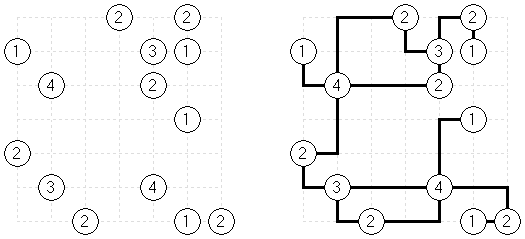
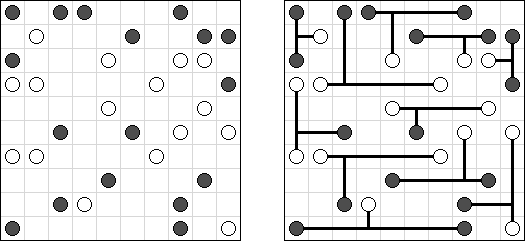
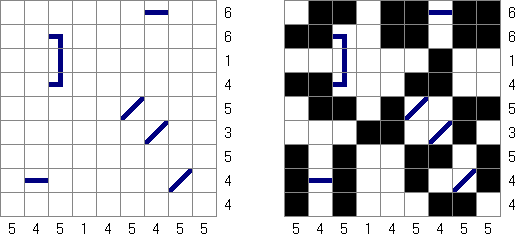
Ichimaga Crossing Ichimaga: the lines may cross other lines; the lines cannot change direction at the point of intersection.
Magnetic Ichimaga ("Jishaku-Ichimaga"): the circles with the same digits cannot be connected.
Snake Multiple Snakes: a grid contains multiple snakes. Head and tail of all snakes are given. Different snakes do not touch each other, even diagonally.
Toroidal Snake: a grid wraps around itself. A snake can go from one edge to another.
Minesweeper Double Minesweeper: place mines into each empty cell in the grid, at most two mines per cell.
Mirukuti Milk Tease is a variation of Mirukuti ("Milk-T") puzzle. T-shaped line may connect:
Two circles of the same color must be connected by the straight-line segment of the T-shaped line.
Light Up Mirror Akari ("!irakAkari!"): a square or rectangular grid contains diagonal walls (black triangles) with mirrors.
Tren Tren+:
Ghost Tren:
Mubunanba Mubunanba+:
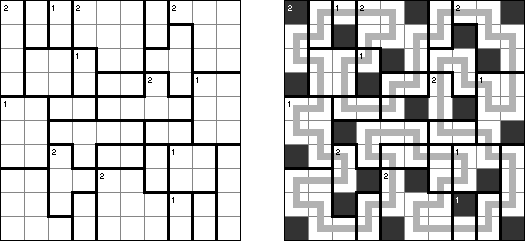
Yajilin Regional Yajilin (also known as "Yajilin (Regions)") is a square or rectangular grid divided into regions. The aim is to blacken some cells and to draw a single non-intersecting loop through all the white cells. A number in a region indicates the number of black cells in that region. A region without a number can contain any amount of black cells. No two black cells can share a border. The loop may visit numbered cells; numbered cells can be blackened.
LITS Double LITS has one difference from the classic variant of the puzzle: each region must contain two tetrominoes. These two tetrominoes within a region cannot touch each other horizontally or vertically (only diagonally); they can be the same or different shapes.
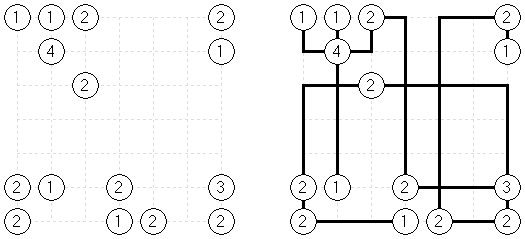
Kapama Sunglasses is a logic puzzle. A rectangular or square grid contains lines ("bridges") in some cells. The goal is to blacken some cells to create pairs of figures (twin shapes). Twin shapes ("lenses") are symmetrical with respect to a bridge. Two lenses may not share an edge. Cells with bridges can not be blacken. Numbers outside the grid show the number of black cells in a corresponding row or column.
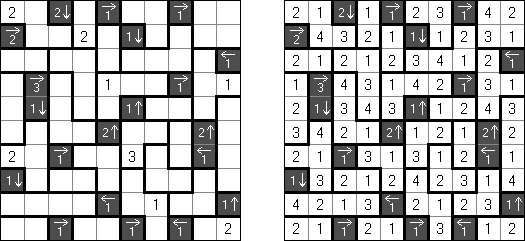
Makaro Masakuchi is a logic puzzle published by Nikoli. A rectangular or square grid is divided into regions. Each region must be filled with each of the digits from 1 to the number of cells in the region. When two numbers are orthogonally adjacent across a region boundary, the numbers must be different. The grid may contain black cells with arrows and numbers: the arrow points at the greatest number among the four cells around (up, under, left, right) the black cell. The number in the black cell shows the difference between the greatest number and the second highest number in all orthogonally adjacent cells around the black cell.
|

![Tapa [Line]](../data/tapa1.gif)
![Tapa [Diagonal Neighbors]](../data/tapa11.gif)